 |
||
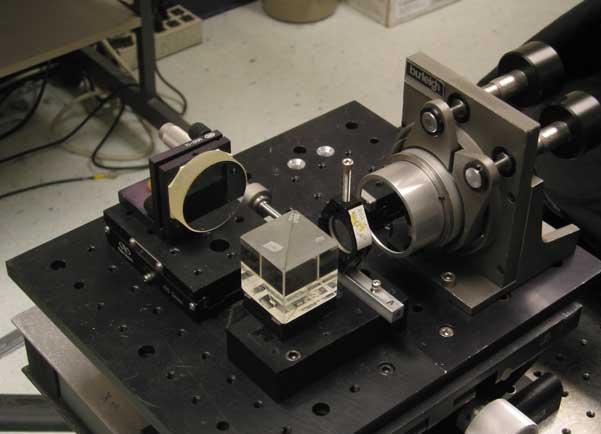
Closeup of the angle-independent fixed delay interferometer. A 1/4 inch thick glass plate (in 1" diameter mount with screw) creates a virtual image of the mirror in the Burleigh mount. When the distance of the other mirror is adjusted to longitudinally superimpose on the Burleigh mirror (through the 40 mm beamsplitting cube), then according to ray paths the mirrors superimpose (and for all angles), but according to time-of-flight there is a 1.1 cm delay. Hence the same time delay is imposed on a wide range of incident angles. This angle independence improves fringe visibility for extended sources such as blurry star images, wide diameter fibers, and spectral pen lamps. In Doppler velocimetry measurements and ~2.5x resolution boosting experiments a single delay is used. In recent experiments achieving 6x boosting the glass plate was changed over a variety of fixed sizes up to ~1 inch thick. |
||
|
||
Site maintained by |
||||

